
Lab manuals for anatomy and physiology are essential guides, offering experiments and observations; they support textbook learning and enhance understanding of complex biological systems.
These resources, often in PDF format, aid students in practical application, fostering a deeper grasp of human body structure and function through hands-on experience.
Purpose of a Lab Manual
Lab manuals serve as structured companions to anatomy and physiology coursework, bridging theoretical knowledge with practical application. Their primary purpose is to provide a detailed, step-by-step guide for conducting experiments, dissections, and observations, ensuring students gain hands-on experience with biological concepts.
These manuals outline specific procedures, materials needed, and expected outcomes, fostering a standardized learning environment. They often include pre-lab questions to assess understanding and post-lab exercises to reinforce learning. Furthermore, lab manuals facilitate the development of critical thinking, problem-solving, and observational skills.
Available in formats like PDF, they detail the anatomy and physiology of various systems, aiding in identification and analysis. They are designed to complement textbooks, offering a focused, practical approach to mastering the intricacies of the human body, and are crucial for allied health and nursing students.
Importance in Learning A&P
The importance of a lab manual in learning Anatomy & Physiology (A&P) extends far beyond rote memorization. It transforms abstract concepts into tangible experiences, solidifying understanding through direct observation and manipulation. Practical application, guided by these manuals – often available as PDF downloads – is vital for retaining complex information about the human body.
Dissections and experiments detailed within foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills, essential for future healthcare professionals. Lab manuals support the textbook material, providing context and reinforcing key principles. They allow students to visualize structures and processes, enhancing comprehension of anatomy and physiology.
For students in fields like nursing and allied health, these manuals are indispensable, building a foundation for clinical practice. They cultivate analytical abilities and prepare students for real-world scenarios, making A&P learning more effective and impactful.
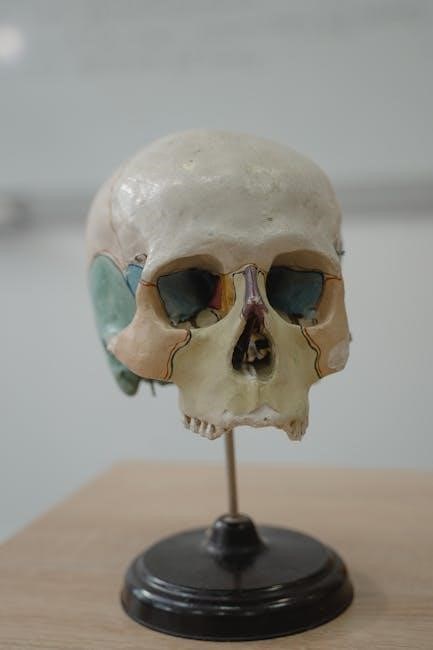
Microscopy and Basic Lab Techniques
Lab manuals detail microscopy, including compound microscope operation, slide preparation, and common staining techniques – crucial skills for visualizing anatomical structures.
Compound Microscope Operation

Lab manuals dedicate significant sections to mastering the compound microscope, a cornerstone of anatomy and physiology studies. These guides typically begin with identifying the microscope’s key components – the ocular lens, objective lenses, stage, condenser, and illumination source.
Detailed, step-by-step instructions are provided for proper setup, including correct illumination adjustment and focusing techniques. Students learn to start with the lowest power objective lens for initial specimen viewing, gradually increasing magnification while carefully utilizing the coarse and fine focus knobs.
Emphasis is placed on calculating total magnification (ocular lens magnification multiplied by objective lens magnification) and understanding the working distance. Lab manuals also address common troubleshooting issues, such as achieving optimal clarity and preventing damage to slides or the microscope itself. Proper cleaning and storage procedures are also outlined to ensure longevity of the instrument.
Preparing Microscope Slides
Anatomy and physiology lab manuals dedicate substantial instruction to proper slide preparation, crucial for clear microscopic observation. These guides detail both wet mount and dry mount techniques, emphasizing the importance of thin specimen sections for optimal light transmission.
Students learn to correctly place specimens on slides, add appropriate mounting fluids, and gently lower coverslips to avoid air bubbles. Specific instructions cover preparing slides from various sample types – tissues, cells, and microorganisms – often including guidance on sectioning techniques using microtomes.

Lab manuals also highlight safety precautions when handling sharp instruments and biological materials. Detailed protocols for staining techniques are often introduced here, preparing students for visualizing cellular structures. Proper labeling and disposal procedures are also emphasized, ensuring organized and safe lab practices.
Common Staining Techniques
Anatomy and physiology lab manuals extensively cover common staining techniques vital for enhancing contrast and visualizing cellular components under a microscope. These manuals detail procedures for stains like methylene blue, used for general cell observation, and eosin, often paired with hematoxylin for tissue differentiation.
Students learn the principles behind differential staining, including Gram staining for bacteria identification and acid-fast staining for mycobacteria. Protocols emphasize proper application, timing, and rinsing steps to achieve optimal results. Safety precautions regarding handling staining chemicals are paramount, with detailed disposal guidelines.
Lab manuals often include expected results for each stain, aiding in accurate interpretation. Furthermore, they may introduce specialized staining methods for specific tissue types or cellular structures, broadening students’ microscopic observation skills and analytical abilities.

Body System Dissections & Observations
Lab manuals guide dissections of the skeletal, muscular, and nervous systems, providing detailed instructions for identification and observation of anatomical structures.
These practical exercises enhance understanding of body organization and function through direct, hands-on exploration.
Skeletal System – Bone Identification
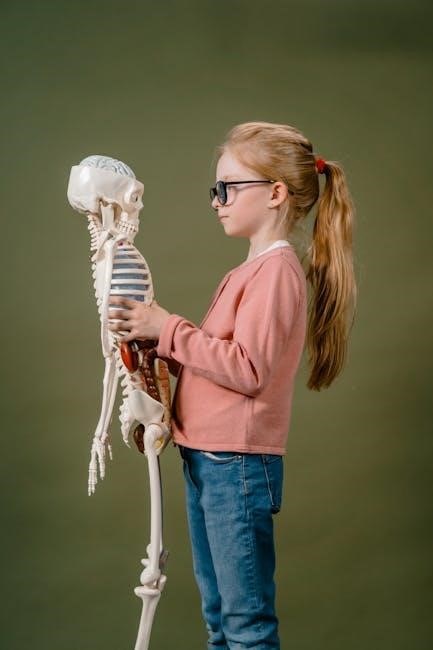

Bone identification within the lab manual is a cornerstone of understanding skeletal anatomy. Students utilize diagrams and often, actual skeletal specimens to learn the names and locations of various bones.
Exercises typically involve identifying bones like the femur, tibia, humerus, radius, ulna, and cranial bones. The manual guides students to differentiate between long, short, flat, and irregular bones, noting key features like processes, foramina, and condyles.
Practical application includes assembling skeletal models and articulating joints. Understanding bone markings is crucial, as these serve as attachment points for muscles and ligaments. The lab component reinforces textbook knowledge, enabling students to visualize and manipulate the skeletal framework, solidifying their comprehension of skeletal structure and function.
Detailed illustrations and clear labeling are essential for accurate identification.
Muscular System – Muscle Tissue Types
The lab manual’s section on the muscular system focuses on differentiating the three primary muscle tissue types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Students learn to identify these tissues under a microscope, observing key characteristics like striations, cell shape, and nucleus count.
Skeletal muscle exhibits striations and multiple nuclei per cell, while smooth muscle lacks striations and has a single, central nucleus. Cardiac muscle displays striations and typically one or two nuclei.
Lab exercises involve examining prepared slides and identifying these features. Understanding the functional differences – voluntary control for skeletal, involuntary for smooth and cardiac – is emphasized. The manual often includes diagrams illustrating muscle fiber arrangements and contraction mechanisms, reinforcing the link between structure and function.
Practical observation enhances comprehension of muscle tissue diversity and its role in body movement.
Nervous System – Brain Dissection
The lab manual guides students through a brain dissection, a crucial component of understanding the nervous system. This exercise allows for the identification of major brain structures, including the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
Students carefully dissect preserved sheep brains, tracing pathways and observing the physical relationship between different regions. The manual provides detailed diagrams and instructions for identifying structures like the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe, and the corpus callosum.
Emphasis is placed on understanding the function of each region and how they contribute to overall brain activity. Observing the meninges and ventricles is also included. This hands-on experience solidifies knowledge of brain anatomy and its correlation to neurological function, enhancing comprehension beyond textbook descriptions.
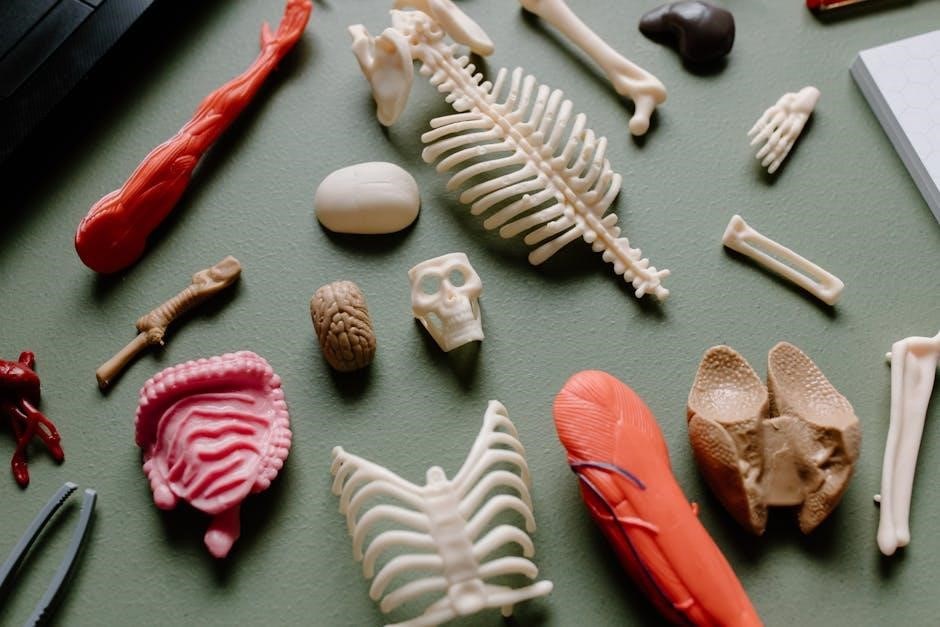

Physiological Experiments
Physiological experiments within the lab manual demonstrate body functions; students measure heart rate, lung capacity, and enzyme activity, applying anatomy & physiology concepts.
These practical exercises reinforce theoretical knowledge, providing tangible data and fostering a deeper understanding of human biological processes.
Cardiovascular System – Heart Rate & Blood Pressure
Cardiovascular experiments in the lab manual focus on assessing heart rate and blood pressure, vital signs reflecting circulatory system efficiency. Students learn to accurately measure these parameters at rest and following physical activity, observing physiological responses.
The manual guides students through understanding factors influencing heart rate – like exercise, posture, and emotional state – and blood pressure – including systolic and diastolic readings.
Analyzing collected data allows for correlation between anatomy (heart structure, blood vessel arrangement) and physiology (blood flow dynamics, cardiac output).
Students may explore the effects of different interventions, such as caffeine or specific exercises, on these vital signs, solidifying their comprehension of cardiovascular regulation.
Proper technique and safety protocols for using sphygmomanometers and pulse oximeters are emphasized, preparing students for clinical applications.
Respiratory System – Lung Capacity
Lab manual exercises concerning the respiratory system center on determining lung capacity, a key indicator of pulmonary function. Students utilize spirometers to measure various lung volumes – tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, and vital capacity.
The manual explains the anatomy of the lungs and the mechanics of breathing, linking structural features to functional measurements. Students learn how these volumes contribute to overall lung capacity and efficient gas exchange.
Experiments often involve comparing lung capacity measurements between individuals with varying characteristics (age, sex, fitness level), analyzing potential influencing factors.
Understanding the relationship between anatomy, physiology, and measurable parameters reinforces concepts of respiratory mechanics and clinical relevance.
Safety guidelines for using spirometry equipment and interpreting results are detailed, preparing students for potential healthcare applications.
Digestive System – Enzyme Activity
Lab manuals dedicated to the digestive system frequently explore enzyme activity, demonstrating the biochemical processes of food breakdown. Experiments commonly investigate the action of amylase, protease, and lipase – enzymes responsible for carbohydrate, protein, and fat digestion, respectively.
Students typically measure reaction rates under varying conditions (temperature, pH, enzyme concentration) to observe how these factors influence enzymatic efficiency. The manual details the anatomy of the digestive tract and the specific locations where each enzyme functions.
These exercises highlight the relationship between physiology and chemical reactions, illustrating how enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of complex molecules into absorbable units.
Data analysis and graphical representation of results are emphasized, fostering scientific skills. Safety protocols for handling enzymes and substrates are clearly outlined.
Understanding enzyme kinetics provides a foundation for comprehending metabolic disorders and the impact of dietary factors.

Lab Safety and Procedures
Lab manuals prioritize safety, outlining rules for handling biological specimens and chemicals; proper disposal protocols and emergency procedures are crucial for a secure learning environment.
General Lab Safety Rules
Safety is paramount in any anatomy and physiology laboratory. Lab manuals consistently emphasize adherence to established guidelines to minimize risks. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including lab coats, gloves, and eye protection, to shield against potential hazards.
Food and beverages are strictly prohibited within the lab space to prevent contamination. Maintain a clean and organized workspace, promptly addressing any spills or broken glassware. Familiarize yourself with the location of safety equipment, such as fire extinguishers, eyewash stations, and first aid kits.
Properly dispose of biological waste according to designated protocols, and never attempt unauthorized experiments. Report any accidents or injuries, no matter how minor, to the instructor immediately. Respectful conduct and mindful awareness of surroundings are essential for a safe and productive learning environment for everyone involved.
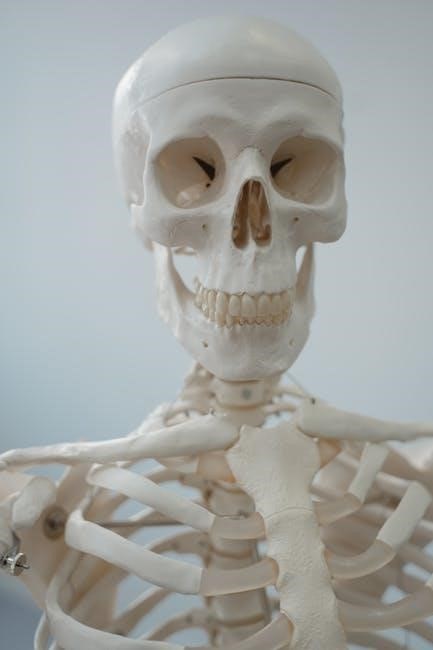
Handling Biological Specimens
Lab manuals provide detailed instructions for the respectful and safe handling of biological specimens. Treat all specimens – preserved or fresh – as potentially hazardous, assuming they may contain infectious agents. Always wear gloves and appropriate PPE when dissecting or observing tissues.
Avoid direct contact with specimens, and never pipette by mouth. Carefully follow dissection guidelines to minimize damage and ensure accurate observations. Properly dispose of biological waste in designated containers, adhering to biohazard protocols.
Thoroughly wash hands with soap and water after handling any biological material, even if gloves were worn. Report any spills or accidental exposures to the instructor immediately. Maintaining a sterile work environment and practicing responsible specimen handling are crucial for both personal safety and scientific integrity.

Resources and Further Learning
Online resources and recommended lab manuals, like those by Allen and Marz, supplement learning; clinical articles and AI tools enhance understanding of anatomy & physiology.
Online Anatomy & Physiology Resources
Numerous online platforms significantly complement traditional anatomy and physiology learning, extending beyond the scope of a standard lab manual. Subscriptions, like those offered by Nursing Times, grant access to over 6,000 peer-reviewed clinical articles, providing real-world context to theoretical concepts. These resources often include exclusive learning units and step-by-step procedures, aiding in the comprehension of complex physiological processes.
Furthermore, the integration of AI-powered tools, such as the “Ask Nursing Times” feature, allows for personalized learning and immediate answers to specific questions. Websites dedicated to anatomy and physiology offer interactive models, virtual dissections, and detailed illustrations, enhancing visualization and spatial understanding. University websites, like the University of Georgia, frequently provide openly accessible lab manuals and supplementary materials created under textbook transformation grants, promoting wider access to quality educational resources.
These digital tools, combined with a solid foundation from a well-structured lab manual, create a dynamic and comprehensive learning experience.
Recommended Lab Manuals (Specific Titles)
Selecting the right lab manual is crucial for a successful anatomy and physiology course. “Laboratory manual for anatomy and physiology” by Allen, Connie (2009) is a frequently cited resource, offering a comprehensive approach to practical learning. Several manuals cater specifically to nursing and allied health students, such as the work by Marz, Kamatchi, DSilva, Prabhakaran, and Chandra, providing relevant clinical applications.
For pharmacy students, practical lab manuals like those used in the B. Pharmacy curriculum at MARRI LAXMAN REDDY INSTITUTE, focus on specific systems like the human ear, integrating charts and models for enhanced understanding. It’s important to note that many institutions create their own customized lab manuals, often available as PDF files, tailored to their specific curriculum and experimental protocols.
When choosing, consider the manual’s clarity, illustrations, and alignment with your course objectives. A well-designed manual will significantly enhance your lab experience.